- Advertising
- Bare Metal
- Bare Metal Cloud
- Benchmarks
- Big Data Benchmarks
- Big Data Experts Interviews
- Big Data Technologies
- Big Data Use Cases
- Big Data Week
- Cloud
- Data Lake as a Service
- Databases
- Dedicated Servers
- Disaster Recovery
- Features
- Fun
- GoTech World
- Hadoop
- Healthcare
- Industry Standards
- Insurance
- Linux
- News
- NoSQL
- Online Retail
- People of Bigstep
- Performance for Big Data Apps
- Press
- Press Corner
- Security
- Tech Trends
- Tutorial
- What is Big Data
The Ultimate Guide to Servers: Find the Best Solution for Your Business
Be it e-commerce, banking, machine learning or real-time analytics, your business depends on server performance and flexibility. Perhaps servers are too complicated to delve into when you have other business priorities. But the server infrastructure should be top of the list as it represents the backbone of any successful business.
To ease your decision, we put together an in-depth guide on servers. You can download it for free or, if you’re in a hurry, read this blog post to find out key information about servers.

Before choosing your infrastructure you need to decide what your business goals are and which server type best suits them. Let’s start with the basics.
What Is a Server?
As one of the most difficult tech words to explain, it sure is used a lot. At its core, a server is a computer. You can run the same software that you run on a computer on a server. Unlike computers, however, servers can do more than what a personal computer or smartphone can; they store data and facilitate communication, both with apps and with other servers.
How Many Types Are There?
There are many types of servers, from file or web server, to FTP or game server. This classification is made from a software point of view. When it comes to your business, you’ll have to consider servers from a platform perspective and decide between dedicated and virtualized servers. Let’s see how they differ.
Dedicated vs. Virtualized Servers
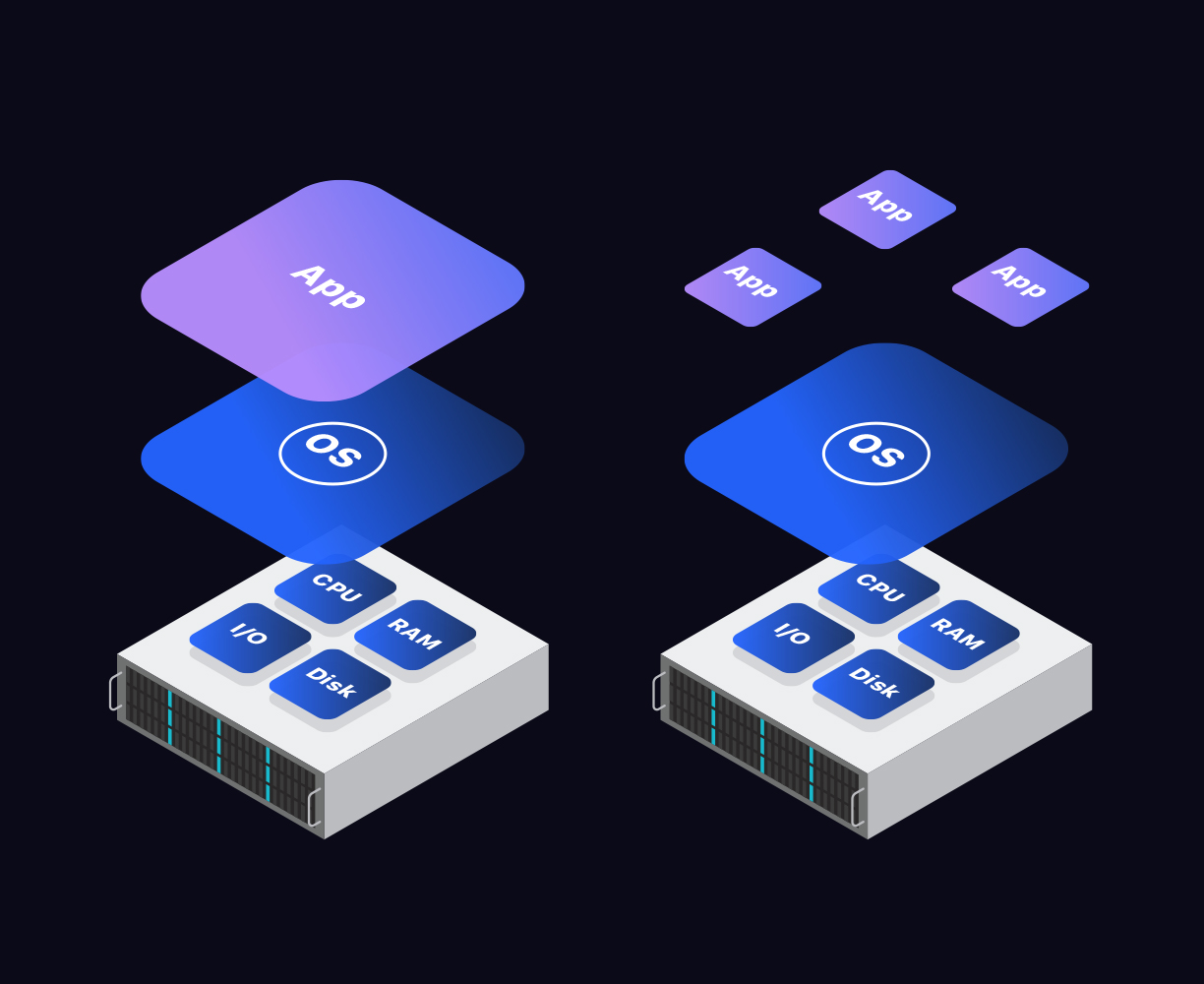
Dedicated servers, or bare metal servers, are physical machines. They have fixed RAM, processor, and hard drive, just as a regular computer, and the operating system is installed directly on the machine. Dedicated servers represent a type of Internet hosting in which you lease an entire machine for yourself, without having to share it with someone else.
Virtualized servers, on the other hand, are software constructs that run on dedicated servers. A virtualized server emulates virtual compute resources like CPU, RAM, disk, and network through a hypervisor that runs and manages several virtual servers.
Each main category splits into two subtypes, since both dedicated and virtualized servers also have a cloud computing platform version.
Virtualized Servers:
- Virtual Private Servers (VPS/VDS)
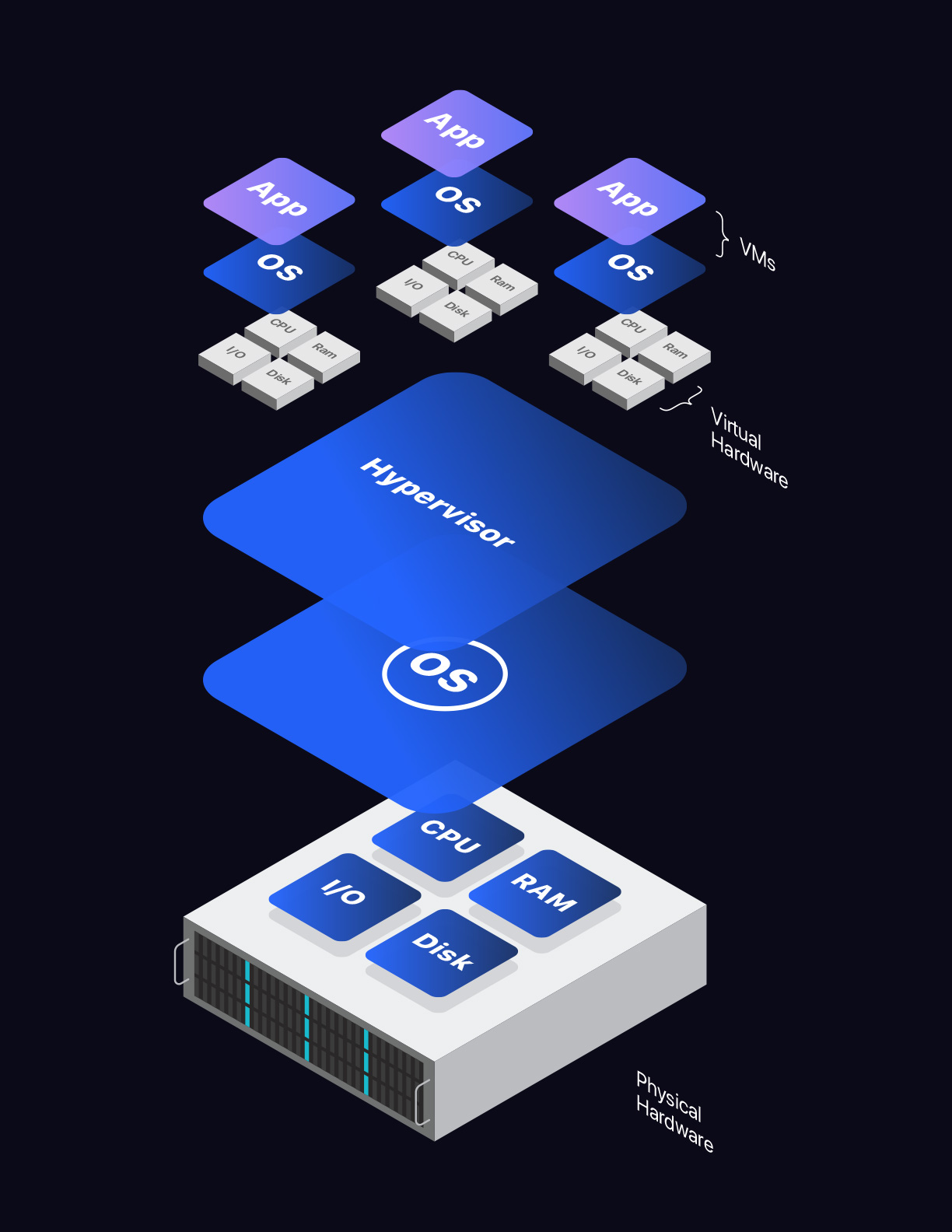
- Virtual Cloud Servers
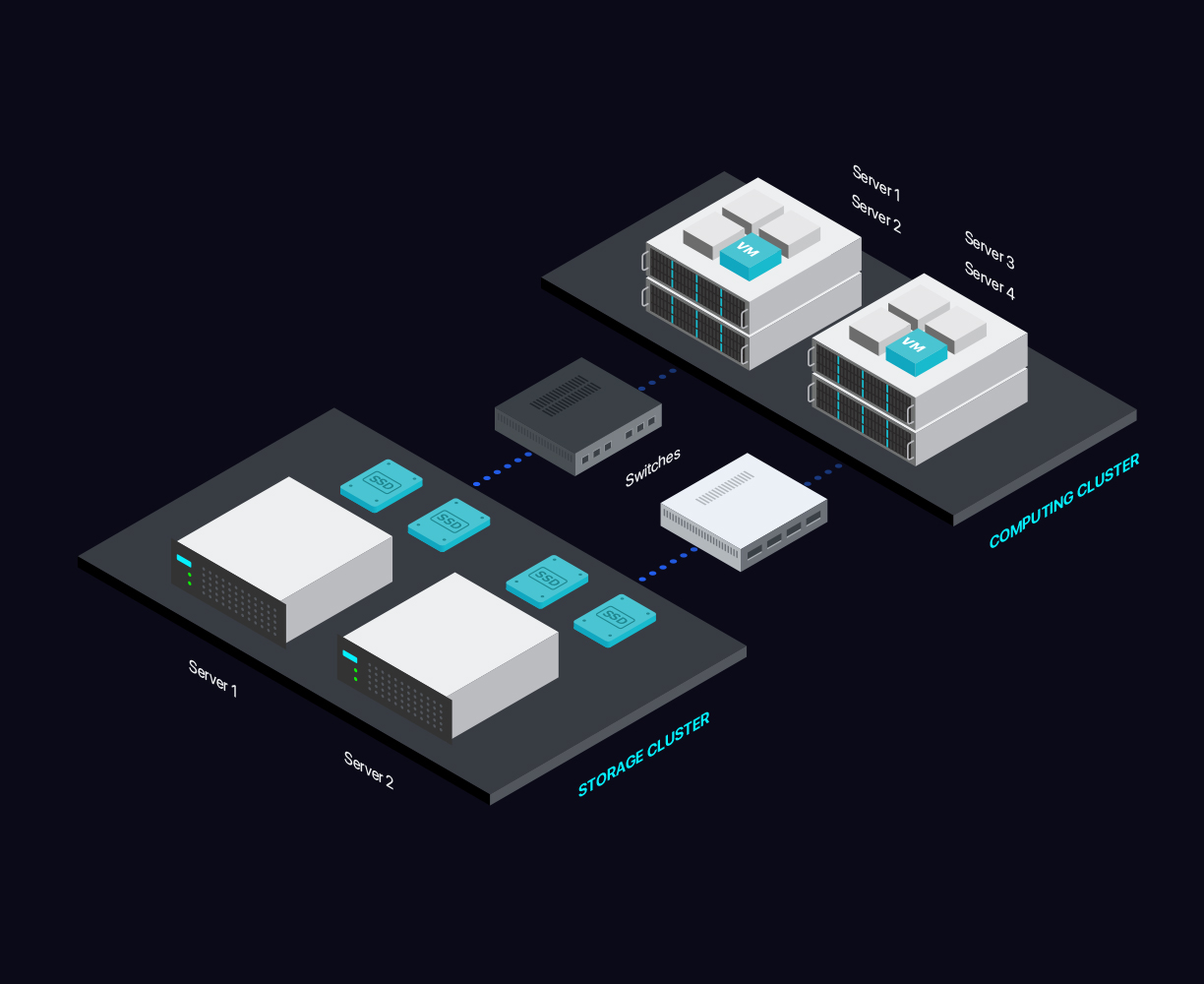
Dedicated Servers:
- Bare Metal Servers

- Bare Metal Cloud Servers
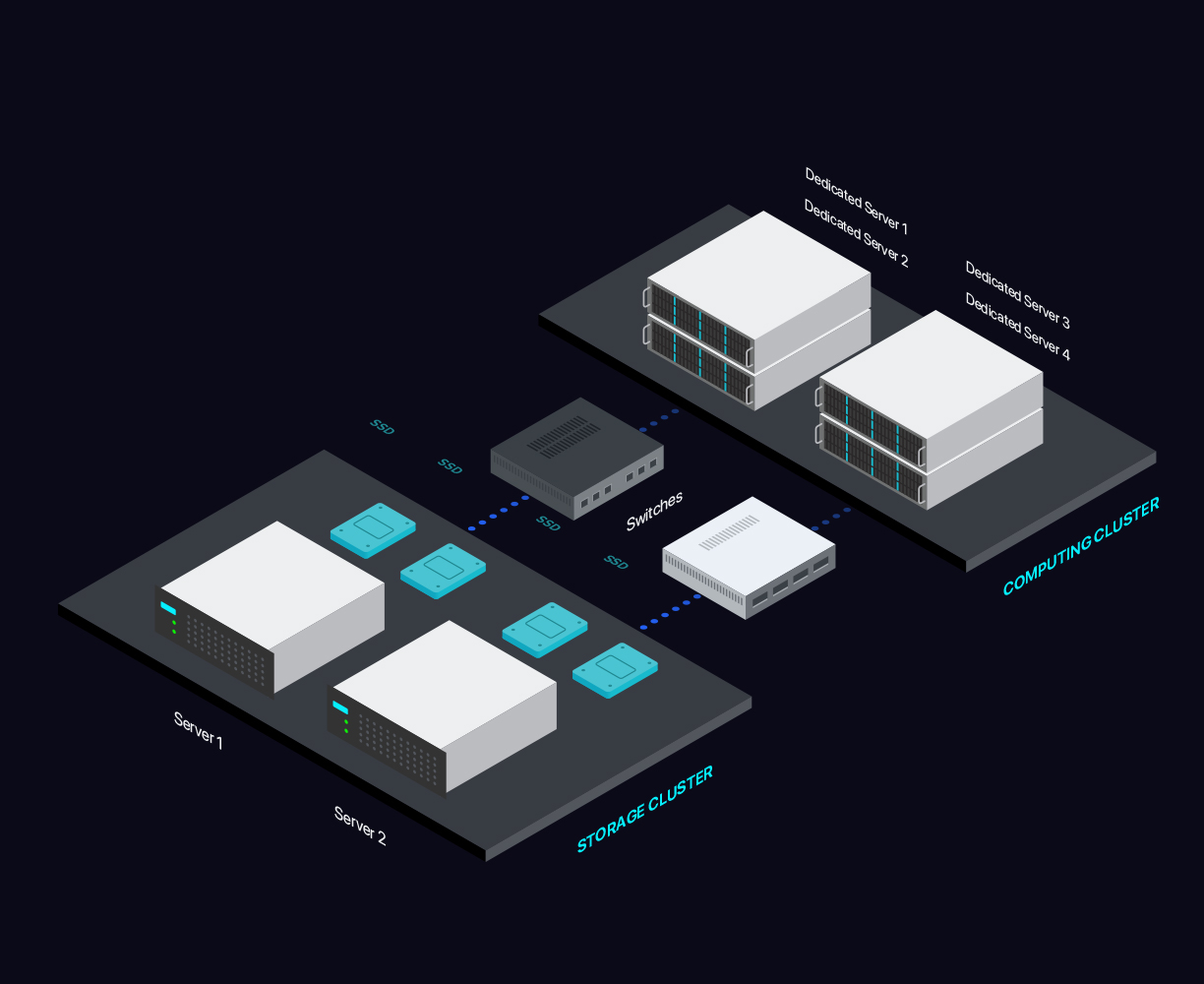
Each server type comes with its advantages and disadvantages. For a detailed view of each, check out our guide.
Which One Is Good for Which Use Case?
While virtualized servers are great for highly variable workloads, physical dedicated servers (bare metal) are great for predictable and data-intensive workloads, or workloads that don't change quickly enough to require the by-the-minute scalability of cloud servers.
Cloud servers are great for big data analytics and IoT due to their hyper-scalability.
When it comes to the bare metal cloud, there’s no limit to its business use cases because it combines the best of two worlds: the performance of dedicated servers and the scalability of the cloud. It’s perfect for all data-intensive workloads, high-transaction workloads that do not tolerate latency, and for storage that is used intensively and frequently. If you’re into e-commerce, app development, banking, gaming, or big data projects, the bare metal cloud will give you the resources and flexibility you need.
Conclusion
It’s daunting to choose between a virtual server, virtual cloud, physical machine, or hybrid as the success of your business rests on the performance of your infrastructure. Remember, it all comes down to your needs and goals, so start there.
Need an extra hand deciding? Download our free guide and take a closer look at a few of the most important criteria to consider: hardware, OS, hypervisor, tenancy, performance, scalability, flexibility, provisioning, speed, system recovery, security, management, deployment type and costs. We also delve deeper into each server subtype and specific use cases to help you navigate the server galaxy with ease and avoid common pitfalls.
Readers also enjoyed:
Modern Storage Technologies in 2020: What You Need to Know


Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.