- Advertising
- Bare Metal
- Bare Metal Cloud
- Benchmarks
- Big Data Benchmarks
- Big Data Experts Interviews
- Big Data Technologies
- Big Data Use Cases
- Big Data Week
- Cloud
- Data Lake as a Service
- Databases
- Dedicated Servers
- Disaster Recovery
- Features
- Fun
- GoTech World
- Hadoop
- Healthcare
- Industry Standards
- Insurance
- Linux
- News
- NoSQL
- Online Retail
- People of Bigstep
- Performance for Big Data Apps
- Press
- Press Corner
- Security
- Tech Trends
- Tutorial
- What is Big Data
Nginx in WHM, what is the best option?
For a long time, the only web server available in WHM was Apache, with Litespeed as a paid premium option. However, Nginx is widely considered today to be superior to Apache, mainly due to the event-driven architecture that allows it to serve a much larger number of connections and handle periods of high server load.
The addition of Nginx to WHM has been often requested by users and a number of unofficial plugins have been developed that implement it to the hosting platform, the most popular of these being Engintron. Starting with version 80, WHM developers have finally added Nginx as an alternative to Apache, but the service is still experimental, and many features can’t be controlled from the interface. In this article, we will compare the performance of this version of Nginx with Engintron.

Installing Nginx from Easyapache
The installation of Nginx is very easy from Easyapache 4, you simply have to activate it from the Additional Packages section, then provision the change. If any flavour of Nginx (such as Engintron) is installed on the server, it should be removed in advance in order to avoid any conflicts.
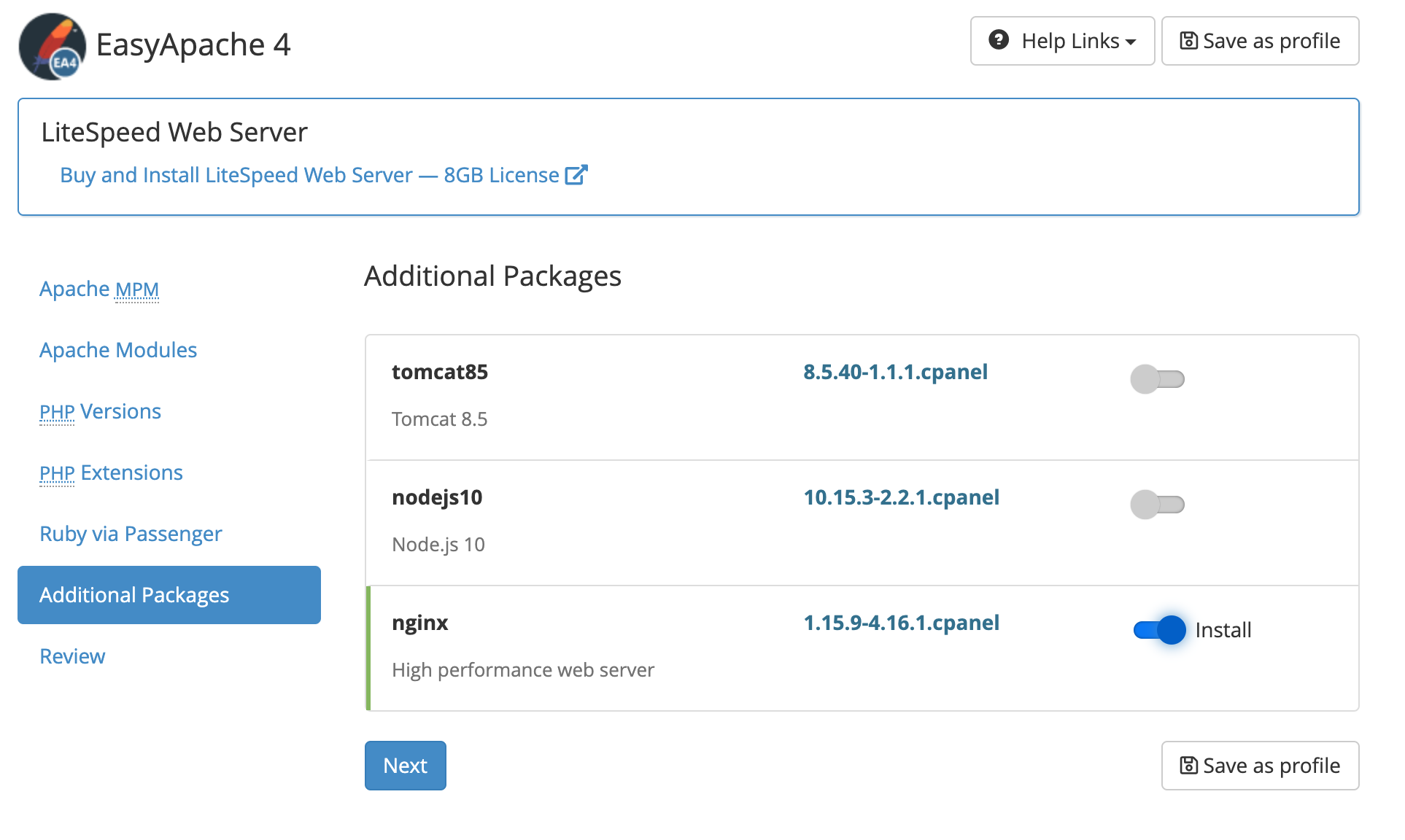
After provisioning, Nginx will be active and listens on the ports 80 and 443. Apache is not fully removed, as it is used by some WHM services, and uses the alternative ports 81 and 444. Since cPanel developers have decided to offer Nginx in order to speed up Wordpress sites, the latest version is installed on the server, with php 7.3 and php-fpm.
We will use the simple benchmarking tool ab (included with every installation of Apache) in order to test the server, with 5000 requests and 200 parallel connections.
Here are the results:
Concurrency Level: 200
Time taken for tests: 225.687 seconds
Complete requests: 5000
Failed requests: 1
(Connect: 0, Receive: 0, Length: 1, Exceptions: 0)
Write errors: 0
Non-2xx responses: 1
Total transferred: 55027324 bytes
HTML transferred: 53949353 bytes
Requests per second: 22.15 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 9027.494 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 45.137 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 238.11 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 39 4606 1622.5 4134 13121
Processing: 149 4338 1512.0 3874 11831
Waiting: 52 1607 941.7 1251 5776
Total: 188 8944 2107.4 8278 19793
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 8278
66% 9042
75% 9912
80% 10917
90% 12141
95% 12789
98% 14823
99% 15167
100% 19793 (longest request)Installing Engintron
Engintron is a free plugin for WHM that integrates Nginx with the other services and includes an easy to use graphical interface. The first step is to customize Easyapache in order to remove Nginx and prepare for the installation of Engintron, which can be done in a few minutes with a simple one-line command:
cd /; rm -f engintron.sh; wget --no-check-certificate https://raw.githubusercontent.com/engintron/engintron/master/engintron.sh; bash engintron.sh install
Unlike the Nginx installed by WHM, Engintron doesn’t actually replace Apache, but rather works as a reverse proxy and caching server in front of it, serving all static content and reducing overall load. This approach has several important benefits: a much higher number of requests can be served, while all Apache configuration files and modules (such as .htaccess directives or modsec rules) continue to work.
No further tweaks are needed after installing Engintron, so we will run the test again, with the following results:
Concurrency Level: 200
Time taken for tests: 201.874 seconds
Complete requests: 5000
Failed requests: 0
Write errors: 0
Total transferred: 56359880 bytes
HTML transferred: 54552420 bytes
Requests per second: 24.77 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 8074.976 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 40.375 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 272.64 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 35 4651 1802.6 4082 10519
Processing: 352 3323 1675.6 3282 12119
Waiting: 72 1275 1086.7 945 9995
Total: 434 7974 1733.9 7304 17362
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 7304
66% 7950
75% 8563
80% 9091
90% 10885
95% 11909
98% 12498
99% 12853
100% 17362 (longest request)As we can notice, Engintron is slightly faster, probably because of its powerful static and dynamic caching features. In a production environment, these features could give Engintron an even greater advantage over plain Nginx. However, WHM’s Nginx also performs very well and can be a solid option for Wordpress installations, even in the current experimental status.
Readers also enjoyed:

An Infrastructure as a Service Serious Wordbook


Leave a Reply
Your email address will not be published.